
If you are one of the 85,000 businesses or 30 million users who rely on Lastpass to help you manage your password, you might have been a wee bit concerned about the recent news headlines about the security breach.
Should you be panicking? Is your data vulnerable? The quick answer is – not if your vault was set up well. But let’s chat through the best practice Lastpass set-up and who might be at risk.
A few FAQs
What information did the threat actors access?
Does this mean they can see all my usernames and passwords?
Could they hack my LastPass password and get into my account?
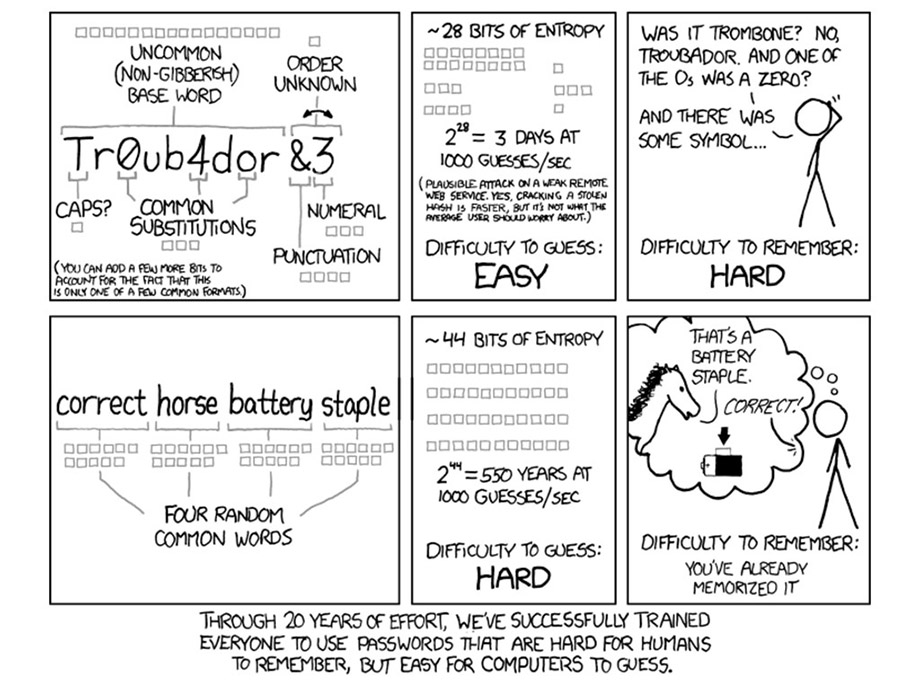
Here is quick visual guide to help you when it comes to choosing a solid password for your account:
What is a federated vault?
Why is that a good thing?
The Colton approach
At Colton, we use a federated login that integrates your O365 account with your Lastpass. That’s why if we have set up your accounts, you don’t get prompted for a password and Duo code each time you log into Lastpass; you already have an authority cookie from logging into O365.
Key Takeaway
Ensure you have good passwords or encryption keys – it makes a difference if a threat actor tries to get their hands on your data.

